Production Deployment
When development and the testing is done, we need to deploy to online machine and then provide services.
Compile
If project code needs to be compiled, though it outputs app/ directory from src/, we suggest to run command npm run compile during deployement, to avoid some unexpected impact. Or pull the latest code in a clean directory and execute the compile command.
If you modify the babel preset, then you need to modify the compile command (babel src/ --presets think-node --out-dir app/) in package.json the corresponding changes.
If the code does not need translation, then deploy src/ directory can be.
Production Environment
When the project is created, a file named production.js is automatically created in root directory, which is the entry file for the production environment and definesenv as production. Never use development.js in the production environment as an entry file to start the service.
Service Management
PM2
PM2 is specific designed module for Node.js service management. PM2 need to be install globally:
sudo npm install -g pm2After installation, we have pm2 command line command.
When project is created, a file named pm2.json is created in root directory, of which content is as bellow:
{
"apps": [{
"name": "demo",
"script": "production.js",
"cwd": "/Users/welefen/Develop/git/thinkjs/demo",
"max_memory_restart": "1G",
"autorestart": true,
"node_args": [],
"args": [],
"env": {}
}]
}Change name to your project name, and modify cwd field to online project path.
Start Project
Run pm2 start pm2.json on project root directory to start application, and you will see the following information:
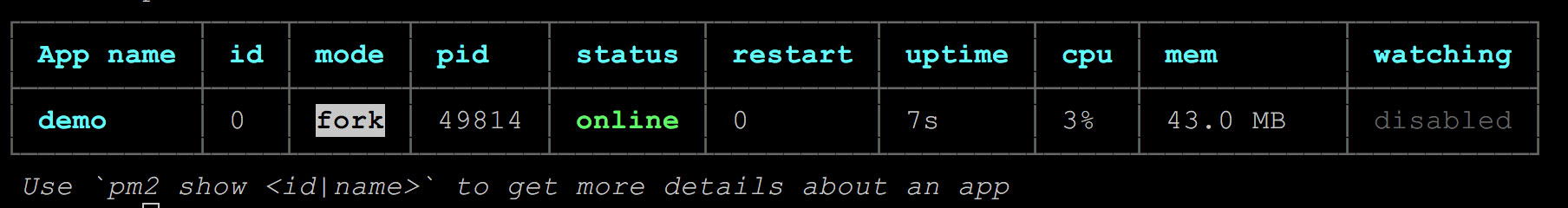
Restart Project
When there is code changed, we need to restart service to make it effective.
The easiest way to restart service is through pm2 restart pm2.json, but this approch can result in temporary service interruptions. (restarting the service takes time and restarting can result in inability to process user requests which cause service interruption). If you don't want service interruption, then you can send a signal to restart, the specific code:
pm2 sendSignal SIGUSR2 pm2.jsonpm2 will send SIGUSR2 singal to framework, after the main process capture this signal, it will fork a new child process for incomming service, and then gradually close previous child process so as to achiveve none-interrupt service restart.
cluster mode
Framework will force the use of cluster, and provide service in master/worker way, so you can't open cluster mode in pm2 (if you open, service will report errors and exist on start up).
Manually manage process
project start
If you don't want to use PM2 to manage service in production environment, you can manually manage it through a script, , first run `node production.js' to start service.
When service is start up and accessible, start service with nohub node production.js &, nohub and & means run service in background, after that you can see a log similar to the following:
$ nohup node production.js &
[2] 1114
appending output to nohup.outAfter seeing the output, press Enter, execute the exit command to exit the current terminal, so the service is running in the background.
After the start is complete, you can see the specific node process by ps aux | grep node:
welefen 3971 0.0 0.3 3106048 46244 s001 S+ 11:14AM 0:00.65 /usr/local/bin/node /Users/welefen/demo/production.js
welefen 3970 0.0 0.3 3106048 46064 s001 S+ 11:14AM 0:00.64 /usr/local/bin/node /Users/welefen/demo/production.js
welefen 3969 0.0 0.3 3106040 46248 s001 S+ 11:14AM 0:00.65 /usr/local/bin/node /Users/welefen/demo/production.js
welefen 3968 0.0 0.3 3106048 46400 s001 S+ 11:14AM 0:00.65 /usr/local/bin/node /Users/welefen/demo/production.js
welefen 3967 0.0 0.3 3106048 46608 s001 S+ 11:14AM 0:00.65 /usr/local/bin/node /Users/welefen/demo/production.js
welefen 3966 0.0 0.3 3106048 46432 s001 S+ 11:14AM 0:00.65 /usr/local/bin/node /Users/welefen/demo/production.js
welefen 3965 0.0 0.3 3106040 46828 s001 S+ 11:14AM 0:00.65 /usr/local/bin/node /Users/welefen/demo/production.js
welefen 3964 0.0 0.3 3106048 46440 s001 S+ 11:14AM 0:00.64 /usr/local/bin/node /Users/welefen/demo/production.js
welefen 3963 0.0 0.2 3135796 40960 s001 S+ 11:14AM 0:00.31 node production.jsThe first few are fork process, the last one is master process.
Restart Service
When the code changes requires restart the service, the easiest way is to find the main process pid, kill the process by kill -9 PID and then restart. If you do not want to interrupt the service, you can send SIGUSR2 signal to the main process to finish:
kill -s USR2 PIDFor example, the master process's pid being printed in log above is 3963, you can kill -s USR2 3963 to restart the service without interruption. Of course, it is troublesome to do so everytime, you can create a simple script for that.
#!/bin/sh
cd PROJECT_PATH; # enter root directory
nodepid=`ps auxww | grep node | grep production.js | grep -v grep | awk '{print $2}' `
if [ -z "$nodepid" ]; then
echo 'node service is not running'
nohup node production.js > ~/file.log 2>&1 &
else
echo 'node service is running'
kill -s USR2 $nodepid 2>/dev/null
echo 'gracefull restart'
fiuse nginx
Although Node.js itself can directly create HTTP(S) services, it is not recommand so in production environment, instead uses WebServer (such as: nginx) in front, which has several benefits:
- Can do better load balancing, such as: the same project, start the service of multiple ports, using nginx to do the load
- Static resources using nginx has higher performance
- HTTPS service performance is higher
When creating a project, a configuration file named nginx.conf is created in the project root directory:
server {
listen 80;
server_name example.com www.example.com;
root /Users/welefen/Downloads/demo/www;
set $node_port 8360;
index index.js index.html index.htm;
if ( -f $request_filename/index.html ){
rewrite (.*) $1/index.html break;
}
if ( !-f $request_filename ){
rewrite (.*) /index.js;
}
location = /index.js {
proxy_http_version 1.1;
proxy_set_header X-Real-IP $remote_addr;
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header Host $http_host;
proxy_set_header X-NginX-Proxy true;
proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade;
proxy_set_header Connection "upgrade";
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:$node_port$request_uri;
proxy_redirect off;
}
location ~ /static/ {
etag on;
expires max;
}
}server_name,root, port field value is configured according to the actual situation, and then the configuration file is soft link to the nginx configuration file directory, and finally restart the nginx service (you can nginx -s reload to reload the configuration file).
If you still want to provide services directly through Node.js, it is also possible to listen directly to port 80 or port 443 (some environments require sudo to listen on these two ports).
HTTPS
Modern websites highly suggest using HTTPS to provide the security of the website content and prevent the content from being intercepted and tampered with. If you do not want to pay for a certificate, you can use the free SSL/TLS certificate provided by Let's Encrypt, which can be found in the article Let's Encrypt 免费好用的证书.
FAQ
Why static resource is not accessible in production environment?
On project initiation, it will auto-generate middleware config file src/config/middleware.js (multi-module project src/common/config/middleware.js). There is a middleware for handling static resources request, but this middleware by default only for development environment, so you will see static resources can not access after going online.
It is recommanded to use nginx to handle static resource online, of which performance will be higher and lower load for Node service. If you still want to use framework to deal with static resource requests, modify src/config/middleware.js to enable this middleware can do so.
module.exports = [
...
{
handle: 'resource',
enable: true // always open, default is `enable: isDev` which means only open in development environment
},
...
]